A Common Platform for Antibiotic Dereplication and Adjuvant Discovery
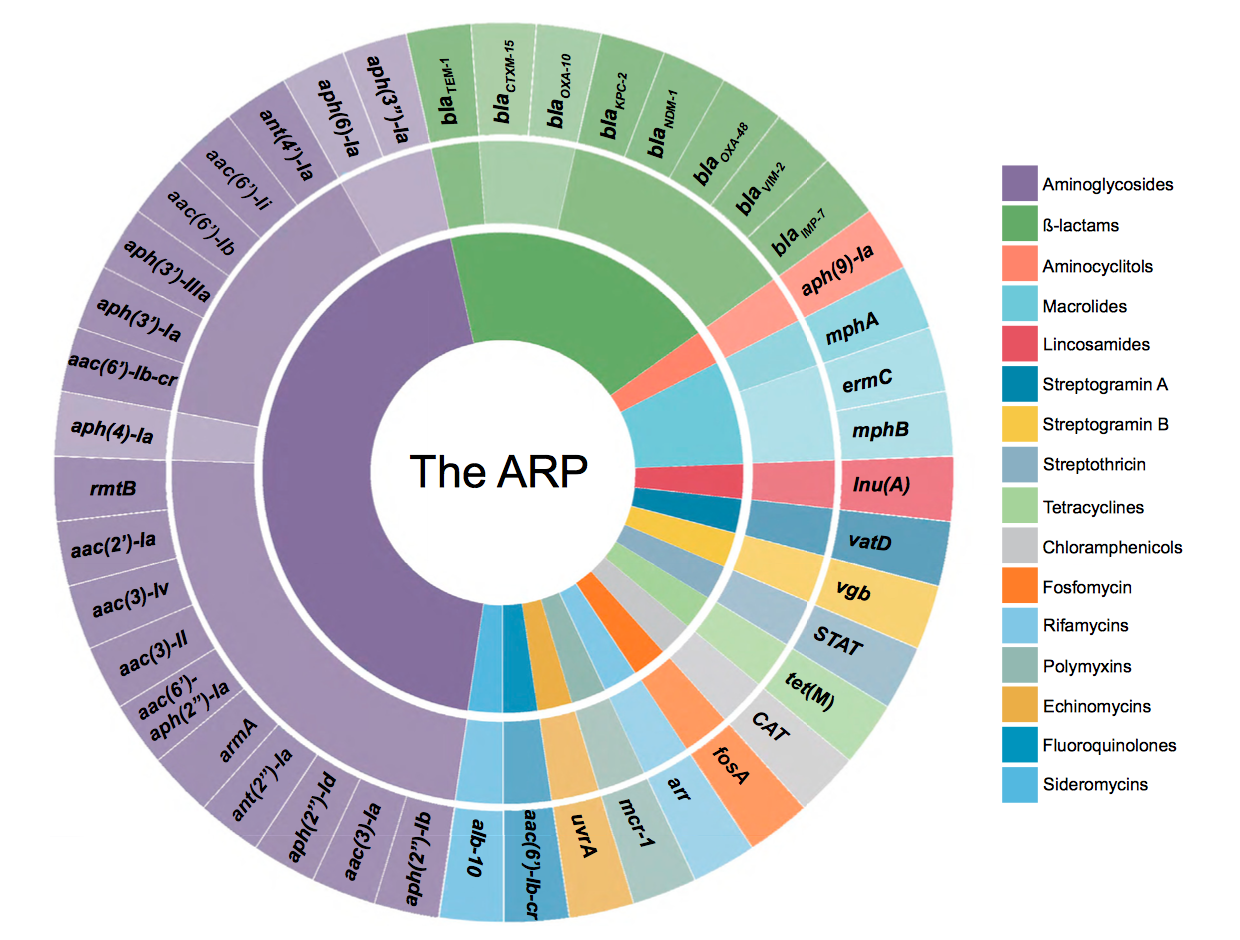
Solving the antibiotic resistance crisis requires the discovery of new antimicrobial drugs and the preservation of existing ones. The discovery of inhibitors of antibiotic resistance, antibiotic adjuvants, is a proven example of the latter. A major difficulty in identifying new antibiotics is the frequent rediscovery of known compounds, necessitating laborious “dereplication” to identify novel chemical entities. We have developed an antibiotic resistance platform (ARP) that can be used for both the identification of antibiotic adjuvants and for antibiotic dereplication. The ARP is a cell-based array of mechanistically distinct individual resistance elements in an identical genetic background. In dereplication mode, we demonstrate the rapid identification, and thus discrimination, of common antibiotics. In adjuvant discovery mode, we show that the ARP can be harnessed in screens to identify inhibitors of resistance. The ARP is therefore a powerful tool that has broad application in confronting the resistance crisis.